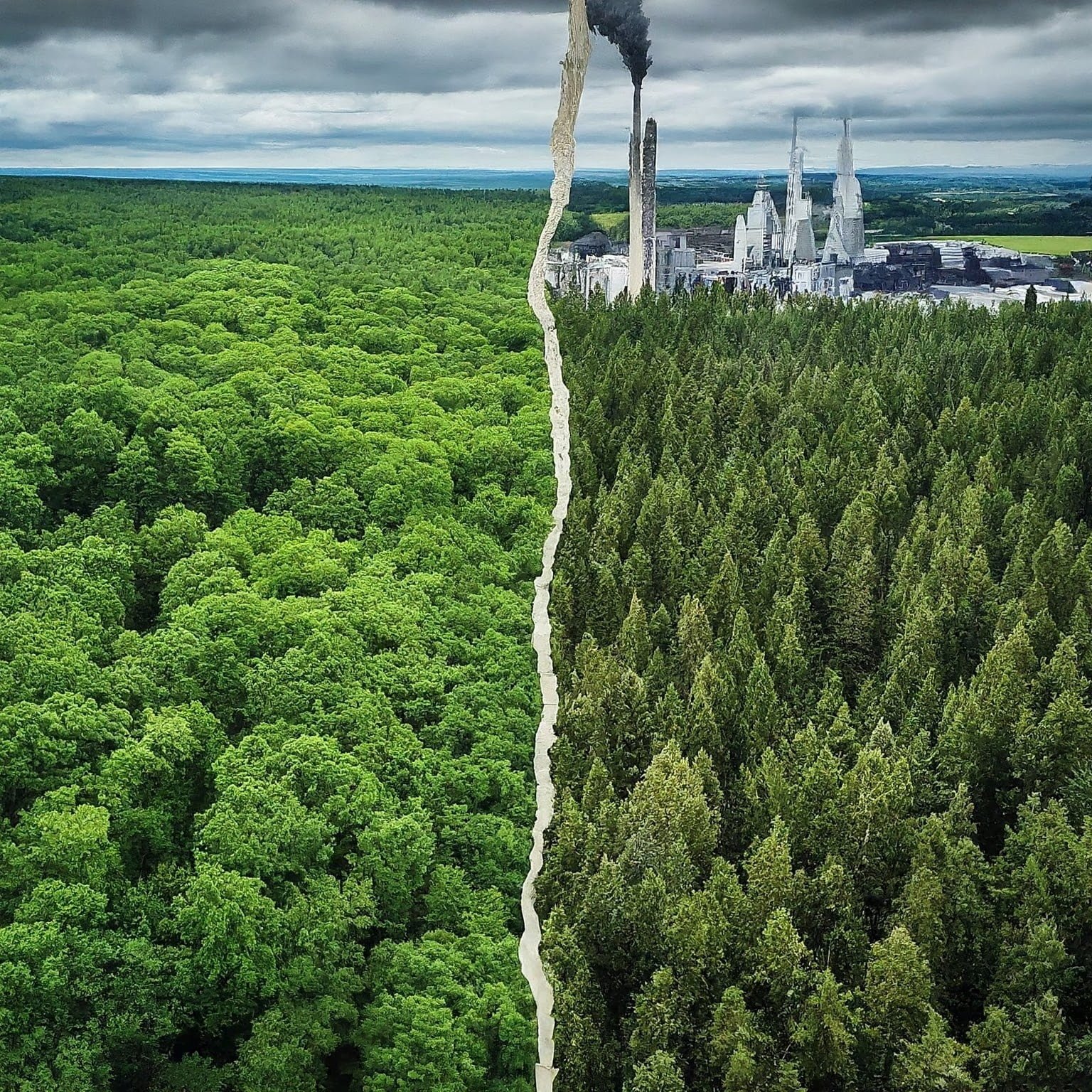
Vietnam’s wood pellet industry has been experiencing phenomenal growth within the last few years. This surge is driven by rising global demand for renewable fuel alternatives, particularly in countries seeking to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. However, this rapid expansion raises urgent questions about its long-term sustainability.
Can Vietnam sustain this boom without compromising its forests, environment, and the future of the industry itself?
The Rise of a Billion-Dollar Industry
Wood pellets are a type of biomass fuel, typically made from compressed sawdust, wood chips, and other forestry residues. Their increasing popularity stems from their status as a renewable energy source that’s considered more environmentally friendly than coal. Key markets like South Korea, Japan, and the European Union are actively seeking alternatives to fossil fuels, leading to a sharp rise in wood pellet demand.
Vietnam has capitalized on this trend. The country’s wood pellet exports have skyrocketed, reaching $354 million in the first half of 2022 alone. The industry is projected to become a billion-dollar export sector for Vietnam in the near future. This growth is fueled by the country’s abundant supply of wood residues from its robust wood processing industry, strategic port locations, and favorable government policies.
The Economic Benefits of Wood Pellets
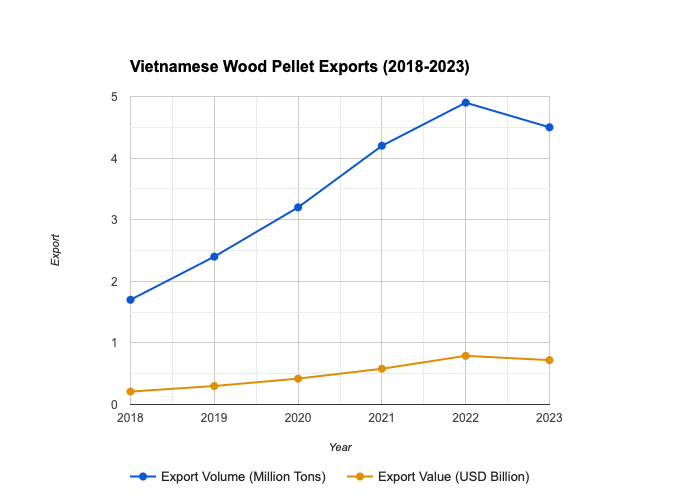
- Vietnam has become one of the world’s leading wood pellet exporters. Wood pellet exports reached 4.9 million tons in 2022 with a turnover of $0.79 billion USD.
- Export volume and value have seen rapid growth in the last few years.
- From 2013 to 2022, export volume increased by 28 times and export value by 34 times.
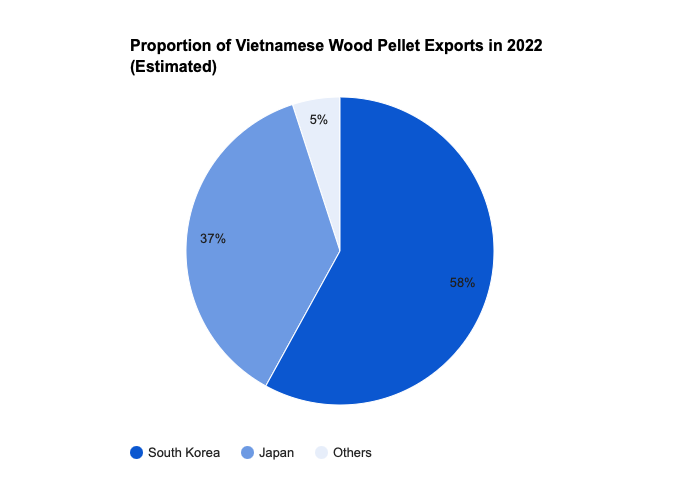
Despite the environmental concerns associated with wood pellet production, there are also economic benefits to consider. The industry has the potential to create jobs and boost local economies, particularly in rural areas where logging and forestry activities are prevalent.
Wood pellet production requires a range of skills and expertise, from forestry management to manufacturing and logistics. This creates employment opportunities for local communities and helps diversify their economies. Additionally, the demand for wood pellets can stimulate the growth of related industries, such as equipment manufacturing and transportation.
Furthermore, the export of wood pellets can generate revenue for countries like Vietnam. As the global demand for green energy continues to rise, there is a growing market for wood pellets in countries that are transitioning away from fossil fuels. By tapping into this market, Vietnam can capitalize on its abundant forest resources and contribute to the global effort to combat climate change.
Sustainability Concerns: Raw Materials and Unregulated Growth
The sustainability issues surrounding Vietnam’s wood pellet boom center primarily on sourcing raw materials and the risks of unsustainable expansion. Here are key areas of concern:
Deforestation Risk:
The production of wood pellets contributes to deforestation and loss of biodiversity in several ways. First, the demand for wood pellets has led to increased logging activities, particularly in countries with large forested areas like Vietnam. This has resulted in the destruction of forests and the displacement of wildlife.
Second, the clear-cutting of forests for wood pellet production disrupts ecosystems and leads to a decline in biodiversity. Forests are home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are unique and endangered. When forests are cleared, these species lose their habitats and are at risk of extinction.
The impact of deforestation and loss of biodiversity goes beyond environmental concerns. Local communities that depend on forests for their livelihoods, such as indigenous peoples and rural communities, are also affected. They lose access to resources like food, medicine, and clean water, and their traditional way of life is disrupted.
Plantation Sources: A large percentage of Vietnam’s wood raw materials come from small-scale acacia plantations that are often poorly managed. This raises questions about long-term sustainability and potential negative environmental impacts associated with monoculture plantations.
Lack of Certification: Many Vietnamese wood pellet producers do not hold internationally recognized sustainability certifications such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC). Without these certifications, it’s difficult to guarantee that wood materials were sourced in an environmentally responsible manner.
Unplanned Expansion: The rapid pace of the wood pellet industry’s growth poses risks of overexploitation. The imbalance between supply and demand can lead to price wars, exploitation of resources, and potentially, long-term instability for the industry.
Balancing Economic Opportunity and Environmental Responsibility
To ensure a sustainable path forward for the wood pellet industry, a balanced approach is needed. This means considering both the economic benefits and the environmental impacts of wood pellet production.
A balanced approach involves implementing strong government regulations that promote sustainability and hold producers accountable. It also requires collaboration between industry stakeholders, including producers, consumers, and environmental organizations. By working together, these stakeholders can develop best practices and standards that prioritize both economic growth and environmental protection.
Furthermore, a balanced approach involves diversifying the energy mix to reduce reliance on wood pellets and other biomass fuels. This can be achieved by investing in other forms of renewable energy, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. By diversifying the energy mix, countries like Vietnam can reduce their carbon emissions and minimize the environmental impact of their energy production.
Vietnam is at a crossroads. The wood pellet boom offers a significant economic opportunity, particularly in rural areas where processing plants can generate jobs. However, pursuing this opportunity without proper safeguards jeopardizes the ecological health and future stability of the industry.
So what can be done?
- Prioritizing FSC Certification: Government bodies and industry leaders must strongly encourage and pursue FSC (or equivalent) certification for wood pellet producers. This globally recognized certification system promotes responsible forest management, ensuring sustainable wood sources and providing market recognition.
- Transparent Supply Chains: Vietnam needs to establish clear and transparent supply chains within the wood pellet industry. This entails rigorous monitoring of raw material sources to ensure they are not contributing to deforestation, and that plantations are managed sustainably.
- Expanding Sustainable Plantations: Investing in expanding well-managed, FSC-certified acacia and other fast-growing plantations could be one solution to increasing sustainable raw material supply. This helps reduce pressure on native forests.
- Incentivizing Sustainability: The government can play a role in offering incentives, both financial and regulatory, to prioritize the production of wood pellets from sustainable sources. This will encourage responsible practices throughout the industry.
The Role of Government Regulations

Government regulations play a crucial role in mitigating the negative impact of wood pellet production. Regulations can help ensure that wood pellets are produced sustainably and that environmental and social standards are met.
Regulations can include requirements for sustainable forestry practices, such as reforestation and biodiversity conservation. They can also set limits on the amount of wood that can be harvested for wood pellet production to prevent overexploitation of forests. Additionally, regulations can address air pollution and worker safety by setting emission standards and occupational health and safety requirements.
Government regulations can also promote transparency and accountability in the wood pellet industry. This can be done through certification schemes and labeling programs that provide consumers with information about the sustainability and origin of wood pellets. By choosing certified wood pellets, consumers can support responsible producers and help drive positive change in the industry.
The Way Forward
Ultimately, the long-term viability of Vietnam’s wood pellet industry hinges on a well-planned transition to a sustainable model. Government policies, industry self-regulation, and consumer demand must align to drive responsible sourcing, transparency, and environmentally conscious production.
It is possible for Vietnam to balance economic growth with sustainability in this industry, but this path requires a concerted and unwavering commitment from all stakeholders.
Originally posted 2024-04-12 16:32:29.


