Fueling Sustainability: The Benefits of Optimizing Calorific Value and Ash Content in Sawdust and Wood Chip Fuel
Sawdust and wood chip fuel are types of biomass fuel that are derived from the waste products of the timber industry. Sawdust is the fine particles that are produced when wood is cut or shaped, while wood chips are larger pieces of wood that have been processed into small, uniform sizes. These types of fuel have gained popularity in recent years due to their renewable and sustainable nature.
Sustainable fuel production is becoming increasingly important as the world seeks to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate the effects of climate change. Biomass fuels like sawdust and wood chips offer a renewable alternative to traditional fossil fuels, as they are derived from organic materials that can be replenished through responsible forestry practices.
The Importance of Optimizing Calorific Value and Ash Content
Calorific value and ash content are two important factors to consider when producing sawdust and wood chip fuel. Calorific value refers to the amount of heat energy that can be produced by burning a specific amount of fuel. It is measured in units of energy per unit of mass, such as megajoules per kilogram (MJ/kg) or British thermal units per pound (BTU/lb). Ash content, on the other hand, refers to the amount of inorganic material that remains after the fuel has been burned.
Optimizing these factors is crucial for sustainable fuel production for several reasons. Firstly, a higher calorific value means that more heat energy can be generated from a given amount of fuel. This leads to increased efficiency and reduced waste, as less fuel is required to produce the same amount of energy. Additionally, a lower ash content means that there is less inorganic material left behind after combustion, resulting in cleaner emissions and reduced environmental impact.
Understanding Calorific Value: What It Means for Sustainable Fuel
Calorific value plays a significant role in the efficiency of fuel. The higher the calorific value, the more heat energy can be produced from a given amount of fuel. This means that less fuel is required to generate the same amount of energy, resulting in increased efficiency and reduced waste.
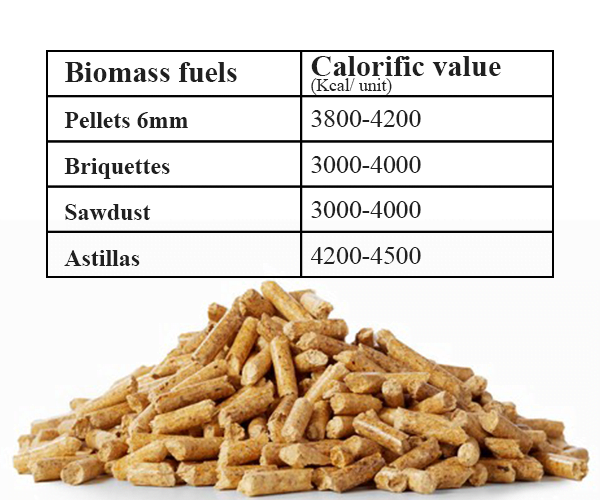
- Sawdust: Sawdust typically has a lower calorific value compared to wood chips due to its finer particle size and potentially higher moisture content. Its calorific value generally ranges from 16 -19 MJ/kg.
- Wood Chips: Wood chips have a higher calorific value than sawdust, usually between 18-21 MJ/kg. This is because they are larger, have lower surface area, and thus tend to have lower moisture content.
In the context of sustainable fuel production, optimizing the calorific value of sawdust and wood chip fuel is crucial. By maximizing the amount of heat energy that can be generated from a given amount of fuel, less waste is produced and fewer resources are required for fuel production. This not only reduces the environmental impact of fuel production but also helps to conserve natural resources.
The Role of Ash Content in Sustainable Fuel Production
Ash content refers to the amount of inorganic material that remains after the fuel has been burned. It is an important factor to consider in sustainable fuel production, as it can affect the quality and environmental impact of the fuel.
- Sawdust: Sawdust can have variable ash content, sometimes higher than wood chips, depending on the wood source and whether it contains bark or other contaminants.
- Wood Chips: Wood chips generally have lower ash content compared to sawdust, typically ranging between 0.5% to 4%. Cleaner wood sources will result in lower ash content.
A lower ash content is desirable in sawdust and wood chip fuel because it means that there is less inorganic material left behind after combustion. This results in cleaner emissions and reduced environmental impact. Additionally, a lower ash content can also improve the efficiency of combustion, as there is less material to impede the flow of air and heat through the fuel.
Benefits of High Calorific Value Sawdust and Wood Chip Fuel
High calorific value sawdust and wood chip fuel offer several benefits for sustainable fuel production. Firstly, they provide increased energy output compared to fuels with lower calorific values. This means that more heat energy can be generated from a given amount of fuel, resulting in greater efficiency and reduced waste.
Furthermore, high calorific value fuels can also help to reduce waste and emissions. By maximizing the amount of heat energy that can be generated from a given amount of fuel, less fuel is required overall. This means that fewer resources are needed for fuel production and less waste is produced. Additionally, the combustion of high calorific value fuels can result in cleaner emissions, as more of the fuel is converted into heat energy and less is released as pollutants.
Increased Efficiency: How Optimizing Calorific Value Reduces Waste
Optimizing the calorific value of sawdust and wood chip fuel can significantly reduce waste in the production process. By maximizing the amount of heat energy that can be generated from a given amount of fuel, less fuel is required overall. This means that fewer resources are needed for fuel production and less waste is produced.
In addition to reducing waste, optimizing calorific value also improves the efficiency of combustion. When more heat energy can be generated from a given amount of fuel, less fuel is required to produce the same amount of energy. This means that more of the fuel is converted into useful heat energy and less is wasted as unburned material or released as pollutants.
Lower Emissions: The Environmental Benefits of Sustainable Fuel
One of the key benefits of sustainable fuel production is its potential to reduce emissions and mitigate climate change. By using renewable biomass fuels like sawdust and wood chips, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and their associated greenhouse gas emissions.
Optimizing sawdust and wood chip fuel can further reduce emissions by maximizing the efficiency of combustion. When more heat energy can be generated from a given amount of fuel, less fuel is required overall. This means that fewer emissions are produced during the combustion process.
Cost Savings: The Financial Impact of Optimizing Sawdust and Wood Chip Fuel
In addition to the environmental benefits, optimizing sawdust and wood chip fuel can also lead to significant cost savings. By maximizing the efficiency of combustion and reducing waste, less fuel is required overall. This means that fewer resources are needed for fuel production, resulting in lower costs.
Furthermore, optimizing sawdust and wood chip fuel can also reduce maintenance and cleaning costs. Fuels with lower ash content produce less inorganic material during combustion, resulting in cleaner emissions and reduced buildup in equipment and chimneys. This can lead to lower maintenance and cleaning costs, as well as improved equipment longevity.
Here’s a breakdown of how optimizing sawdust and wood chip fuel use can lead to significant cost savings. While exact figures vary depending on numerous factors, here’s the general picture:
Areas of Cost Savings:
- Fuel Procurement:
- Moisture Content: Reducing moisture content significantly increases fuel efficiency per unit, meaning you need less fuel to generate the same heat. A 10% reduction in moisture can lead to fuel cost savings of 5-15% or more.
- Bulk Purchasing: Negotiating larger-volume contracts with suppliers often leads to discounts per unit of fuel.
- Sourcing: Finding alternative, lower-cost sources of sawdust or wood chips (e.g., sawmill waste vs. processed chips) can yield significant savings.
- Logistics and Transportation:
- Local Sourcing: Using local suppliers reduces transportation costs, which can be a major expense.
- Optimized Delivery Schedules: Consolidating deliveries to optimize truckloads reduces per-trip costs.
- Equipment Efficiency and Maintenance:
- Fuel Quality: Using cleaner fuels with lower ash content reduces wear and tear on boilers/furnaces, leading to lower maintenance costs and longer equipment life.
- Matching Fuel to Equipment: Calibrating equipment to the specific calorific value and ash content of your fuel source ensures optimal burn efficiency.
- Ash Reduction and Disposal:
- Lower Ash Fuels: Switching to fuels with naturally lower ash content significantly reduces ash disposal costs.
- Ash Utilization: Exploring options to sell ash as a byproduct (for fertilizer, building materials, etc.) can offset disposal costs or even generate revenue.
Example Figures:
- A facility switching from processed wood chips (50% moisture content) to locally-sourced sawmill sawdust (30% moisture content) could reduce fuel volume requirements by approximately 25%, leading to significant annual savings.
- Optimizing logistics to consolidate deliveries and reduce transportation distances could result in 5-15% savings on transportation costs.
- Switching to a fuel with 2% less ash content may extend boiler cleaning intervals, saving thousands of dollars per year in maintenance and downtime costs.
Sustainable Fuel for Industrial Applications: The Role of Calorific Value and Ash Content
Sustainable fuel production is particularly important for industrial applications, where large amounts of energy are required. Calorific value and ash content play a crucial role in determining the quality and suitability of fuel for industrial use.
High calorific value fuels are desirable for industrial applications because they provide increased energy output. This means that more heat energy can be generated from a given amount of fuel, resulting in greater efficiency and reduced waste. Additionally, fuels with lower ash content are preferred, as they produce cleaner emissions and reduce the risk of equipment damage or downtime due to ash buildup.
Best Practices for Optimizing Sawdust and Wood Chip Fuel
There are several best practices that can be followed to optimize the calorific value and ash content of sawdust and wood chip fuel. Firstly, it is important to ensure that the raw materials used for fuel production are of high quality. This means selecting wood that is free from contaminants and has been properly dried to reduce moisture content.
Secondly, the size and uniformity of the fuel particles can also affect its calorific value and ash content. It is important to process the wood into small, uniform sizes to ensure consistent combustion and minimize ash production.
Finally, proper storage and handling of the fuel can also help to maintain its quality. It is important to store the fuel in a dry environment to prevent moisture absorption, which can reduce calorific value and increase ash content.
The Future of Sustainable Fuel Production
In conclusion, sawdust and wood chip fuel offer a renewable alternative to traditional fossil fuels for sustainable fuel production. By optimizing the calorific value and ash content of these fuels, we can increase efficiency, reduce waste and emissions, and achieve significant cost savings.
As the world seeks to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate the effects of climate change, sustainable fuel production will play an increasingly important role. By utilizing renewable biomass fuels like sawdust and wood chips, we can reduce our environmental impact and move towards a more sustainable future.
Originally posted 2024-04-01 12:25:00.