Sawdust and wood chips offer a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to coal, providing cleaner combustion, lower emissions, and renewable sourcing, thereby contributing to greener energy solutions.
Why Sawdust and Wood Chips are the Future of Industrial Fuel
The industrial sector is one of the largest consumers of energy, and as the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change and environmental degradation, there is an increasing need for sustainable energy sources. Traditional fossil fuels such as coal and oil are not only finite resources but also major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. As a result, there has been a growing interest in alternative energy sources that are renewable, carbon-neutral, and have a lower environmental impact.
One such alternative is biomass energy, which utilizes organic materials such as sawdust and wood chips as fuel. Biomass energy has gained traction in recent years due to its numerous advantages and potential to meet the growing demand for sustainable energy in the industrial sector.
The Advantages of Sawdust and Wood Chips as Industrial Fuel
Sawdust and wood chips are highly suitable as industrial fuel due to their high energy content and low moisture content. These materials have been used for centuries as a source of heat and energy, and their properties make them ideal for industrial applications. The high energy content of sawdust and wood chips means that they can produce a significant amount of heat when burned, making them an efficient fuel source.
In addition to their high energy content, sawdust and wood chips also have consistent quality and availability. These materials are byproducts of the forestry and wood processing industries, which means that they are readily available in large quantities. This consistent availability ensures that industries can rely on a steady supply of fuel without disruptions.
Furthermore, sawdust and wood chips have low emissions and environmental impact compared to traditional fossil fuels. When burned, these materials release carbon dioxide, but since they are derived from organic sources, the carbon emitted is part of the natural carbon cycle. This makes biomass energy carbon-neutral, meaning that it does not contribute to the net increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels. Additionally, the emissions from burning sawdust and wood chips are generally lower in sulfur and nitrogen compared to fossil fuels, reducing air pollution and its associated health risks.
Availability and Accessibility of Raw Materials
One of the key advantages of using sawdust and wood chips as industrial fuel is the abundance of these materials as byproducts of the forestry and wood processing industries. These industries generate large quantities of waste in the form of sawdust and wood chips, which would otherwise be disposed of or left to decompose. By utilizing these waste materials as fuel, industries can reduce waste and make use of a resource that would otherwise go to waste.
Moreover, the local sourcing of sawdust and wood chips reduces transportation costs and environmental impact. Since these materials are often available in close proximity to industrial facilities, there is no need for long-distance transportation, which can be costly and contribute to carbon emissions. Local sourcing also helps support local economies and reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels.
Here’s a comparison table of sawdust, wood chips, and coal, focusing on their use as fuels:
| Feature | Sawdust | Wood Chips | Coal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calorific Value | Moderate (16-19 MJ/kg) | Higher (18-21 MJ/kg) | High (15-30 MJ/kg ) |
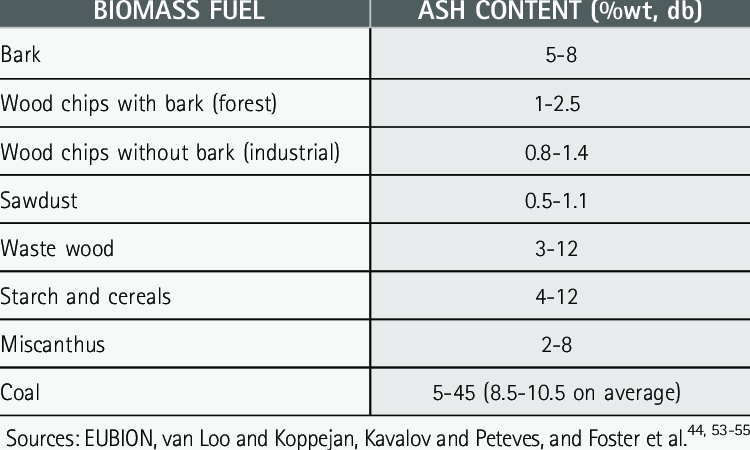
| Ash Content | Variable, can be high | Lower (0.5-4%) | High, variable |
| Sulfur Content | Low | Low | Variable (can be high) |
| Moisture Content | Variable, can be high | Lower | Variable |
| Availability | Waste product, widespread | Waste product, widespread | Mined resource |
| Renewability | Renewable | Renewable | Non-renewable |
| Emissions | Lower CO2, variable particulates | Lower CO2, variable particulates | Higher CO2, SO2, heavy metals |
| Combustion Equipment | Specialized boilers/furnaces | Specialized boilers/furnaces | Specialized power plants/boilers |
| Cost | Can be very affordable | Affordable | Variable, depends on type and market |
Cost-Effective Alternative to Fossil Fuels
In addition to their environmental advantages, sawdust and wood chips offer cost savings compared to traditional fossil fuels. The cost of biomass fuel is generally lower than that of coal or oil, making it an attractive option for industries looking to reduce their energy costs. This cost advantage is particularly significant in regions where biomass resources are abundant, as it reduces the reliance on expensive imported fossil fuels.
Furthermore, the use of sawdust and wood chips as industrial fuel can lead to reduced maintenance and operational costs. Unlike fossil fuel combustion systems, biomass energy systems do not produce ash or other byproducts that require costly disposal or treatment. This not only saves money but also reduces the environmental impact associated with waste disposal.
Reduced Carbon Footprint and Environmental Impact
One of the most significant advantages of biomass energy is its ability to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprint. As mentioned earlier, biomass energy is carbon-neutral, meaning that the carbon emitted during combustion is part of the natural carbon cycle. This is in contrast to fossil fuels, which release carbon that has been sequestered for millions of years, contributing to the net increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels.
By utilizing sawdust and wood chips as fuel, industries can significantly reduce their carbon emissions and environmental impact. This is particularly important in sectors such as manufacturing and power generation, which are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. By transitioning to biomass energy, these industries can play a crucial role in mitigating climate change and reducing their environmental footprint.
Additionally, the use of sawdust and wood chips as industrial fuel reduces waste and landfill usage. Instead of disposing of these materials or leaving them to decompose, they are utilized as a valuable resource. This not only reduces the strain on landfills but also helps conserve natural resources by making use of waste materials.
Improved Efficiency and Energy Output
Biomass energy systems can be highly efficient and provide consistent energy output. Unlike solar or wind energy, which are intermittent sources, biomass energy can be generated continuously, providing a reliable source of heat and power. This reliability is particularly important for industries that require a constant supply of energy for their operations.
Furthermore, biomass energy systems can be designed to maximize efficiency through co-generation and combined heat and power (CHP) systems. Co-generation involves the simultaneous production of electricity and useful heat from the same energy source, while CHP systems generate electricity and useful heat in separate processes but utilize waste heat from electricity generation for heating purposes. These systems can significantly increase the overall efficiency of biomass energy production, making it an even more attractive option for industries.
Versatility and Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure
Another advantage of biomass energy is its versatility and compatibility with existing industrial infrastructure. Biomass energy systems can be integrated with existing facilities, allowing industries to transition to sustainable energy sources without major infrastructure changes. This compatibility makes it easier and more cost-effective for industries to adopt biomass energy, as they can utilize their existing equipment and infrastructure.
Furthermore, biomass energy can be used for various applications, including heating, cooling, and electricity generation. This versatility allows industries to meet their energy needs using a single fuel source, reducing the complexity and cost associated with managing multiple energy sources. For example, sawdust and wood chips can be used in boilers to generate steam for heating or electricity generation, or in absorption chillers for cooling purposes.
Growing Market for Bioenergy and Wood-Based Products
The demand for sustainable energy sources and wood-based products is growing rapidly, creating opportunities for innovation and growth in the biomass energy sector. As governments and industries around the world commit to reducing their carbon emissions and transitioning to renewable energy sources, the market for biomass energy is expected to expand significantly.
In addition to energy production, there is also a growing demand for wood-based products such as biofuels, bioplastics, and biochemicals. These products can be derived from the same biomass feedstocks used for energy production, further increasing the value and economic viability of biomass energy systems. The development of new technologies and processes for converting biomass into these value-added products presents exciting opportunities for the biomass energy sector.
Government Policies and Incentives Supporting the Use of Biomass Energy
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in promoting the use of biomass energy in the industrial sector. Many countries have set renewable energy targets and implemented feed-in tariffs or other financial incentives to encourage the adoption of renewable energy sources. These policies provide a favorable market environment for biomass energy projects and help attract investment.
Furthermore, carbon pricing and emissions regulations also support the use of biomass energy by creating a financial incentive to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By assigning a cost to carbon emissions, governments encourage industries to transition to low-carbon or carbon-neutral energy sources such as biomass. This not only helps mitigate climate change but also creates a level playing field for renewable energy sources in the market.
Challenges and Limitations of Implementing Sawdust and Wood Chips as Industrial Fuel
While there are numerous advantages to using sawdust and wood chips as industrial fuel, there are also challenges and limitations that need to be addressed. One of the main challenges is the upfront capital costs and infrastructure requirements associated with biomass energy systems. Building or retrofitting facilities to accommodate biomass fuel can be expensive, especially for industries that are already operating on tight budgets.
Additionally, the availability and accessibility of sawdust and wood chips can vary depending on the region. While these materials are abundant in some areas, they may be limited or not available at all in others. This can pose a challenge for industries looking to transition to biomass energy, as they may need to rely on imported feedstocks or explore alternative biomass sources.
Furthermore, competition with other biomass feedstocks can also be a limitation. While sawdust and wood chips are highly suitable as industrial fuel, there are other biomass materials such as agricultural residues and energy crops that can also be used for energy production. The availability and cost of these alternative feedstocks can influence the competitiveness of sawdust and wood chips in the market.
The Promising Future of Biomass Energy in the Industrial Sector
Despite the challenges and limitations, biomass energy has the potential to play a significant role in meeting the growing demand for sustainable energy sources in the industrial sector. The advantages of sawdust and wood chips as industrial fuel, including their high energy content, consistent quality, low emissions, and environmental impact, make them an attractive option for industries looking to reduce their carbon footprint and energy costs.
Furthermore, the availability and accessibility of raw materials, cost-effectiveness compared to fossil fuels, improved efficiency and energy output, versatility and compatibility with existing infrastructure, and the growing market for bioenergy and wood-based products all contribute to the promising future of biomass energy in the industrial sector.
With continued innovation and investment, the challenges and limitations of implementing sawdust and wood chips as industrial fuel can be overcome. Governments, industries, and stakeholders need to work together to create a supportive policy environment, invest in research and development, and promote the adoption of biomass energy. By doing so, we can accelerate the transition to a sustainable and low-carbon future in the industrial sector.
Originally posted 2024-02-01 13:53:37.